From escalators in airports to HVAC systems in hospitals and even EDM machines to cricket bowling machines, induction motors are used across a wide range of industrial applications. When selecting a motor, its energy efficiency is a key point of consideration. Energy efficiency is the measure of how much of the input electrical energy gets converted to mechanical energy by the motor. A highly efficient motor will consume less energy to yield the desired output of mechanical energy.
Motor classes and their efficiency
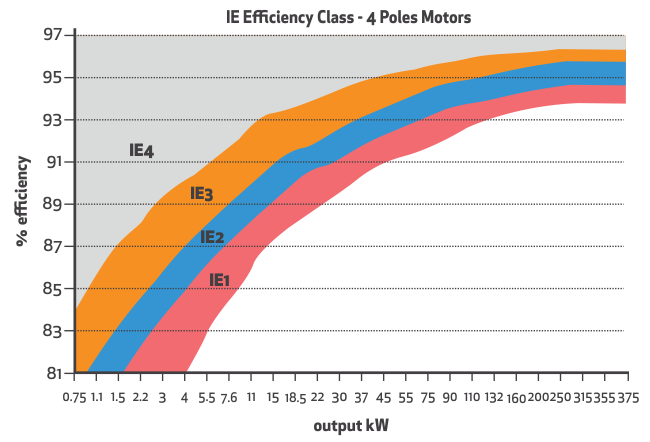
Based on their energy efficiency, the IEC International Efficiency 60034-30-1 standard classifies motors into 4 International Efficiency classes.
IE1: Standard efficiency motors
Speed range: 500 rpm to 3600 rpm
Frequency: 50Hz to 60Hz
Frame size: Aluminum -56 to 200/ cast iron 80 to 400
Regulation standards: IEC 60034-30, IEC 60034-2-1.
IE2: High-efficiency motors
Speed range: 1000 to 3600 rpm
Frequency : 50Hz to 60Hz
Frame size: Aluminum 80 to 160/ cast iron 80 to 400
Regulation standardsIEC 60034-30 and IEC 60034-2-1.
IE3: Premium Efficiency motors
Speed range: 750 to 3600 rpm
Frequency: 50 Hz to 60 Hz
Frame size: Aluminum 80 to 160/ cast iron 80 to 400
Regulation standards: IEC 60034-1-30
IE4: Super premium efficiency
Speed range: 750-3600 rpm
Frequency50Hz to 60 Hz
Frame size Aluminum 100-160/ cast iron 100-315
Regulation standards: IEC 60034-30-1.
Impact of motors on energy saving
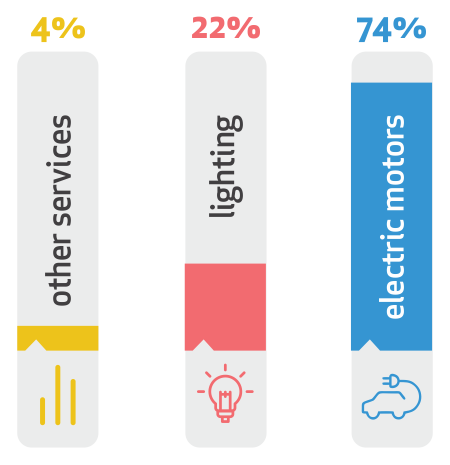
In industrial applications, motors remain the biggest consumers of energy for any business. Industrial production consumes around 42% of the total electricity produced in the world. Further, electrical motors account for around 74% of the total energy consumed by the industry Thus, even a small increase in the energy efficiency of the motor will result in significant energy savings.
Consider how motor optimization compares to other energy-saving measures
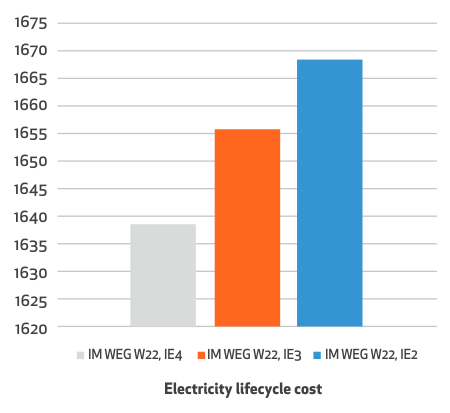
To illustrate with an example, consider the difference of efficiency between 4-pole motors of IE2 and IE 3 classes. An IE 2 motor has an efficiency of around 92-3% whereas an IE3 motor has an efficiency of around 93.6%. These motors could be running continuously in say a warehouse conveyor belt, operating for 3500 hours for an entire year. In that case, the more efficient IE3 motor will save around 1580 kWh of energy over the year.
A case study of motors in pumping
Improved energy efficiency and reduction of carbon footprints are two key returns that can be derived by shifting from IE2 to IE3 motors. A recent study by the Ural Federal University in Russia on motors for pumping applications demonstrated the same.
Pumps make up between 50%-60% of the energy costs in any application. Induction motors are used widely in centrifugal pumps as these pumps do not need their drives to provide a wide speed-range adjustment, a high starting torque, or enhanced dynamic performances.
The studies showed that If a pump’s IE2 motor is replaced with IE3 motor, a total of 82.4MWh energy is saved over 20 years. The study found that the savings in energy costs are around $13511 per year for over 20 years. At the same time, the payback period was around 5.2 years, and the carbon emissions were reduced by 3.78 tons per year.
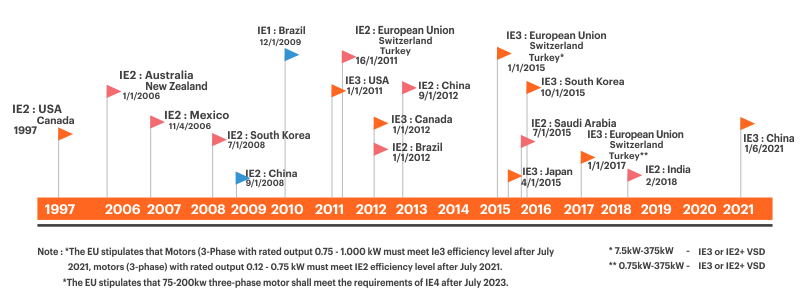
Recognizing the energy-saving potential, the world is rapidly moving towards more efficient motors since the early 2000s. Around 42countries which represent 76% of the world’s energy consumed by motors have adopted the IE2 and IE3 motors as minimum legal requirements for over a decade.IE4 is set to be the minimum legal standard in Europe from July 2023 for motors rated 75–200kW.
Adaption of efficient motors in India
India is currently aiming to cut its carbon emissions to battle climate change. Improving the efficiency of motors is playing a key role in the strategy to achieve this goal. Currently, the industrial sector consumes close to 40% of the total electricity produced in India while electric motors use up around 28% of the national electricity. To put it in numbers, motors consume around 200-220 billion Kwh of electricity in India.
India has banned IE1 motors since October 2017, effectively making IE 2 and higher motors the minimum requirement. As cited by the International Copper Association India, The market share of IE1 and substandard motors stood at around 56% in 2018. Since the ban, it has declined to around 8% in 2020. In the same period, the share of Ie3 motors has increased, with IE4 motors making an appearance in the Indian market.
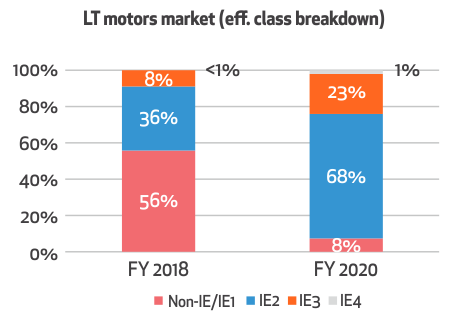
Adapting the IE3 premium efficiency motors could help the Indian industry save an estimated 9000 GWh of energy and save INR 40 billion (over $600 million) spent on energy bills-about one-third of the energy use in India. Additionally, it will help the nation reach its target of a 35% reduction in carbon emissions by 2030.
Most developed countries adopted the IE2 motors in the early 2000s and moved to IE3 in the 2010s. China adopted IE2 in 2012, and moved to IE3 in 2021. However, India made IE2 minimum legal requirement only in 2017. Now, the country is rapidly ramping up its manufacturing capacity to move to IE3 motors. As of 2020, 60% of all motor manufacturing licenses issued in India under IS12615 standard are for manufacturing IE3 motors. This 60% of manufacturers are contributing to over 80% of IE3 motor manufacturing. Apart from improvements to the manufacturing capacity, India also needs an adequate number of NABL accredited laboratories for IE3 motor testing.
Conclusion
While India shifts to IE 3 motors, there is a need to make quality IE3 motors available at competitive prices. Backed by over 2 decades of experience and expertise, Pranshu Electricals is one of the leading motor manufacturers working to resolve this issue. We offer specialized custom IE3 motors in desired quantities and at competitive prices. Capable of working across a wide range of applications, Pranshu has developed specialized induction motors below 60 db for use in defense.
To know more, get in touch with us!

